The slope intercept selection is a linear equation utilized in algebra and analytical geometry to recommend the equation of a straight line. It’s significantly helpful for locating the equation of a line after everyone knows the numerical values of the slope and y-intercept. An equation of a line is one via which all components on that line fulfill the equation. The equation of the road may also be expressed in three completely totally different varieties.
- Stage-Slope Sort
- Intercept Sort
- Two-Stage Varieties
The shape different relies upon upon the given data and the specified end consequence. Nonetheless, the slope intercept selection is a well-liked totally different amongst college faculty college students attributable to its simplicity.
We’ll give consideration to the definition and system of the slope intercept selection on this textual content and research to derive the equation with many examples to know this idea clearly.
Definition and Rationalization of Slope Intercept Sort
The slope-intercept selection is a risk to search out out the straight-line equation in two dimensions. We’ll want a slope or angle of inclination and y-intercept to hunt out the equation of the straight line by means of this technique. This fashion is customary on account of it makes it simple to check off slope and the y-intercept with out drawing the road on a graph.
Allow us to interrupt the slope-intercept thought into two components.
1. The slope of a Line is printed on account of the ratio of the change all through the y-axis to the change all through the x-axis. It’s represented by the image m.
![]()
2. Y-intercept is a stage on the y-coordinate the place a straight line intersects the y-axis. The y-intercept coordinates are expressed as (0, b).
System for Slope-Intercept of the Line
The next equation of a slope intercept selection may very well be utilized to guage a straight-line equation.
y = mx + b
Correct proper right here:
- m = slope or steepness of a line.
- b = y-intercept (a stage the place a line crosses or cuts the y-axis).
- (x, y) = The coordinates of a stage lie on a line.
Derivation of Slope-Intercept Equation
Allow us to check to get the equation of the slope-intercept selection (y = mx + b).
Think about a line L with a slope m crossing the y-axis at a distance of b objects from the origin O.
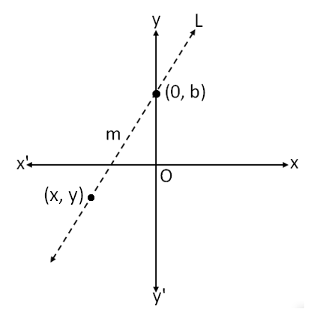
To hunt out the slope of line L that passes by means of the weather (0, b) and (x, y), we’ll use the slope system:
∴ m = (y2 – y1) / (x2 – x1)
Place the given values all through the equation of slope.
m = (y – b) / (x – 0)
m = (y – b) / (x)
Multiply “x” on each side.
mx = y – b
Add “b” on each side of the equation.
mx + b = y – b + b
mx + b = y
(or)
y = mx + b
That’s the standard kind of the slope intercept.
Altering the Widespread straight-line equation into the Slope-Intercept Sort
The equation of slope-intercept may be derived from the major equation of a line all through the next methodology.
The Widespread equation for a straight line is
Ax + By + C = 0
Isolate the value of “y” on one aspect of the equation.
By = – Ax – C
Divide “B” by every time interval.
y = (- A/B) x + (- C/B)
That’s the type of slope-intercept selection.
Correct proper right here (- A/B) is the slope and (- C/B) is the y-intercept (b) of the road.
Solved Examples of Slope Intercept Sort of a Line
Allow us to grasp the most effective methods to compute the equation of a straight line from its slope-intercept selection.
Event 1:
Uncover the equation of a line with a slope of – 4 and a y-intercept of two.
Choice:
Step 1: Determine the slope m and y-intercept b of the road.
Given:
Slope (m) = – 4
Y-intercept (b) = 2
Step 2: Use the slope intercept selection and place the given values in it.
y = – 4x + 2
That’s the required equation of a line.
Event 2:
Write the equation of a line that passes by means of the intention (-2, 5) with a slope of -2.
Step 1: Decide the slope (m) and y-intercept (b) of the road.
Correct proper right here,
m = -2
(x, y) = (-2, 5)
Step 2: Place the given values all through the slope intercept equation to hunt out out b.
5 = -2 (-2) + b
5 = 4 + b
b = 1
Step 3: Now put the value of b and m into the system of slope intercept selection.
y = – 2x + 1
That’s the equation of the road that passes by means of the intention (-2, 5) with a slope of -2.
Event 3:
Decide the equation of a straight line that passes from the weather (2, 4) and (6, 8).
Choice:
Step 1: Calculate the slope of the given line at first.
m = (8 – 4) / (6 – 2)
m = 4 / 4
m = 1
Step 2: Allow us to pick the primary given diploma (2, 4) to hunt out the value of b.
∴ y = mx + b
4 = (1) (2) + b
b = 2
Step 3: Place the value of b and m all through the slope intercept equation.
y = 1x + 2
That is the equation of the road that passes from the weather (2, 4) and (6, 8).
You can too use a slope intercept calculator to unravel the issues of discovering equation of the road to get the ends in couple of seconds.
Conclusion
On this textual content, we have now talked in regards to the introduction of slope intercept selection after which we expanded this idea to an aesthetic diploma. We now have now explored the system for slope-intercept selection and located the most effective methods to get it. We reworked the final word equation of a line into the type of a slope intercept. We solved fully completely totally different examples that will assist you to hunt out out the equation of the road with ease.
